Varicose veins during pregnancyis the proliferation of venous veins that arise during pregnancy and are associated with pathology. It is manifested by severity, paresthesia, pain in the lower extremities and external genitals, swelling, muscle twitching, nutritional skin damage. It is diagnosed by examination, ultrasound angiography. During pregnancy, treatment is usually limited to compression therapy that includes sleep and rest adjustment, physical activity, and nutrition. Perhaps the appointment of pulmonary tonics, skin protection drugs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents. Surgical treatment is usually used after the baby is born.
General information
Varicose veins (varicose veins) is one of the most common vascular diseases associated with pregnancy. According to studies, up to 15-20% of people suffer from venous disease, while 2/3 of them are women, and 60-80% of venous ectasia cases arise due to pregnancy. This disease is usually first diagnosed in young patients, 75% of whom are under 30 years old. In more than two thirds of cases, varicose clinics launch after the 20th week of first pregnancy. The relevance of the timely diagnosis of varicose veins is associated with an increased risk of fetal failure and the risk of fatal thromboembolic complications if adequate therapy is not available.
Reason
Taking into account the statistics on the frequency of varicose veins during pregnancy, most specialists in obstetrics and gynecology consider the disease as a complication of pregnancy. The prognostic factor for vascular ectasia in 91% of patients is a genetic impairment of the middle vein envelope, in which collagen levels are reduced and polysaccharides content increases. The development of varicose veins in women susceptible to pregnancy during pregnancy is facilitated by:
- Increases circulating blood. The increase in BCC in pregnant women ranges from 30-50% (when carrying one child) to 45-70% (if there are 2 or more pregnancies in the uterus). This compensation mechanism allows to ensure adequate supply of blood to the baby, the vital organs of the woman and the fetal system.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the ovaries and placenta secrete more progesterone and relaxin. Under the action of these hormones, the smooth muscle fibers of the veins dilate, and structural regeneration of connective tissue occurs. As a result, the vessel wall copes worse with the increase in venous pressure.
- Compression of a fetal vessel. The growing uterus presses on the lower and pelvic vein. The flow of blood from the pelvis and lower extremities is impaired, the pressure in the lumen increases, straining the venous walls. This factor's influence plays a key role in the development of varicose veins after 25 weeks of pregnancy.
- Changes in hemostasis. As labor approaches, the blood's fibrinolytic activity decreases and the number of clotting factors increases. This adaptive mechanism is intended to reduce the physiological loss of blood volume during labor. This increases the likelihood of a blood clot forming in the veins under a pathological change.
Another factor that contributes to the onset of varicose veins in pregnant women is decreased physical activity. When skeletal muscles are not working properly, blood stagnation in the legs and pelvis increases. The situation is exacerbated by being overweight, in which the volume of blood circulating in the patient's vascular bed becomes even higher.
The mechanism of the pathogenesis
The starting point of the development of varicose veins during pregnancy is the compensatory disruption of the valve apparatus of the venous network. Due to an increase in BCC and a mechanical obstruction to flow from the lower extremities, when the main veins are squeezed, the blood increases pressure on the vessel wall. Hereditary connective tissue failure is enhanced by the relaxation of vascular smooth muscle under the action of progesterone. As a result, the lumen dilates, the valves stop closing, blood is accumulating in the vascular system of the lower extremities. As the disease progresses, the pathological process can spread to the blood vessels of the vulva, vagina, and small pelvis.
Category
The main criterion for codifying various types of venous insufficiency is the anatomical rate of venous stagnation and the severity of the disease. This approach allows for different treatment of treatment regimens for different variants of the disorder to be selected. Taking into account the involvement of various organs in the process, it is possible to distinguish varicose veins of the lower extremities, varicose veins of the vulva, varicose veins of the pelvic organs. According to the severity of clinical symptoms, later stages of dilatation of the lower limb vein are distinguished:
- Compensated varicose veins. With no outward signs of vascular ectasia, pregnant women reported fatigue at the end of the day, discomfort in the calf muscles during brisk walking and movement.
- Compensated inferior varicose veins. A vascular pattern ("star") appears on the skin. At night, swelling of the legs, nighttime cramps, numbness and soreness. Bruises and scratches take longer to heal than usual.
- Decompensated varicose veins. Patients often worry when their legs are hurt and swollen more and more. Visibly enlarged veins, knotted. Hyperpigmentation. There are signs of eczema and nutritional disorders.
With pelvic varicose veins in pregnant women, the disease also develops in stages. In the early stage, the diameter of the affected vessels in any venous plexus of the pelvis does not exceed 5, 0 mm. With the second, the uterus or ovaries participating in the process, the lumen is 6, 0-10, 0 mm. The third type is characterized by the appearance of veins above 10 mm with the participation of all pelvic venous plexus.
Symptoms of varicose veins
In 80-82% of patients, the onset of a feeling of heaviness, tension, "buzzing" in the legs, increases at night and during exertion. The symptoms of varicose veins increase gradually. As the disease progresses in some muscle areas, pain occurs, first develops when standing for a long time, performing physical tasks. In the most severe cases, the pain becomes constant and its intensity can be so pronounced that the woman has difficulty moving independently. Up to 60% of patients with leg muscle cramps, up to 40-50% - loss of sensitivity, leg numbness, up to 30% - itching.
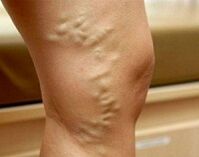
At the stage of compensatory lower varicose veins, external signs of dilation of superficial veins appear. First, areas of mesh vessels and telangiectasias ("mesh" and "stars") are formed on the skin. Then the vein pattern becomes different. The veins look dilated, contracted, and eventually nodules. The spread of ectasia to deep vessels is evidenced by the presence of edema in the tarsus and lower leg joints. With the decompensation of varicose veins, the skin on the feet looks hyperpigmentation, and eczema develops. If the disease arises long before pregnancy, it is possible to have subcutaneous adipose tissue dystrophy, nutritional ulcer.
In 4% of patients, the disease affects the veins of the vulva, vagina, and small pelvis. With varicose veins in the vulva and vagina, a feeling of discomfort, bloating, heaviness, itching can be observed in the external genital area. Possible swelling of the episiotomy and labia, contact vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse. Pelvic congestion syndrome is manifested by pulling or aching pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lower back, sacrum, groin, and external genitalia. Shortness of breath (pain during intercourse) is characteristic. In severe cases, an indigestion disorder is detected.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, varicose veins in pregnant women can be complicated by the development of trophic ulcers, haloitis, thrombophlebitis, superficial thrombosis, anddeep, thrombosis of the pulmonary artery and other major vessels during labor. In 40-45% of cases, placental insufficiency occurs with acute and chronic fetal hypoxia. In 25% of patients, labor abnormalities are observed (weakness of labor, detection of contractile activity of the uterine muscles). With vaginal varicose veins, major trauma can occur in the postpartum period. Nearly one third of women in labor have defects in the process of separating the placenta and having the placenta. The long-term consequence of varicose veins during pregnancy is hemorrhoids, which cause chronic venous insufficiency and pelvic pain.
Diagnosis
With the appearance of characteristic skin markers, the diagnosis of varicose veins during pregnancy usually does not come with any problems. The task of the diagnostic phase is to determine the stage and localization of venous ectasia, to rule out other possible causes of vascular stagnation of the lower extremities. The most informative survey methods are:
- Test Chair. Research shows characteristic changes in the veins in the vulva area and on the inner thigh - angina, age spots, nodules. Swollen labia and perineum may occur. When looking in a mirror, the vaginal mucosa looks enlarged, cyanotic. Vaginal tunnel when touching your hands is smooth, often painful.
- USDG of intravenous systems. During an ultrasonic scan, the shape and diameter of the vessels, their length, anatomical position and condition of the vessel wall are assessed. This method allows you to determine the branching areas, the consistency of the valve device, the ventilation of the veins, the presence and direction of reflux. Both the lower limb and lower aorta can be taken (IVC ultrasound).
- Bilateral scan of leg veins. The advantage of the non-invasive method, which combines traditional ultrasound and Doppler studies, not only obtains detailed information about blood flow parameters but also visualization of the venous network. Duplex angiography is used to comprehensively assess the state of shallow, perforation and deep vessels.
Radiological diagnostic methods (intravenous tomography, selective ovarian scans, progressive chiropractic imaging, pelvic lung scans, CT computed tomography, computed tomography, v. v. . ) during pregnancy is used to a limited extent due to possible negative effects on the fetus. In difficult cases, with suspicion of pelvic varicose veins, diagnostic laparoscopy is carried out with caution. Differential diagnosis of varicose leg veins is made with ascites of pregnant women, heart failure, lymphedema, acute thrombosis of the venous system. Varicose veins of the small pelvis must be differentiated from genital endometriosis, chronic inflammatory pathology of the pelvic organs, inferior and posterior uterine muscular tumors, cysts and other ovarian tumors. In addition to the supervision of an obstetrician and gynecologist, the patient should consult with a cardiologist, cardiologist and oncologist.
Treatment of varicose veins during pregnancy
The main goal of the treatment of varicose veins in pregnant women is to prevent the progression of the disorder, mitigate the severity of the clinical picture and prevent possible thromboembolic complications. happening. Non-pharmacological methods are considered preferable, if necessary, supplemented with pharmacotherapy in the safe stages of pregnancy:
- Compression Therapy. A woman who has been diagnosed with varicose veins should wear it daily throughout pregnancy, using an elastic bandage, special tights or compression socks 1-2 compression during birth and postpartum. Compression therapy by mechanically reducing the diameter of the superficial veins increases the rate of blood circulation, reduces swelling and congestion.
- Herbal remedies and skin protectors. The effectiveness of the use of drugs of this group is associated with an increase in the tonicity of the venous wall, a decrease in its permeability, an improvement in microcirculation, rheological properties of blood and lymph. The advantage of most bioflavonoids is that they can be used during pregnancy and lactation. Blood tonics are prescribed both in the form of tablets and for external use.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. When there are indications of an increased tendency to coagulate and the threat of development of DIC, drugs with antithrombotic activity are used with caution. To improve the rheology of blood and vascular microcirculation, pharmaceutical agents have been shown to suppress platelet aggregation and have a protective effect on the vessels.
Pregnant women with varicose veins are encouraged to use special complex physiotherapy exercises, lymphatic drainage massage, dose walking, incremental contrast showersday. Dietary modification involves consuming foods high in fiber and vegetable fats. Injection therapy, minor ablation, resection, endothelial laser coagulation and other surgical treatments are used in special cases with severe forms of the disease, severe pain syndrome, and presenceof complications. Usually, corrective surgery is performed towards the end of the lactation period.
Distribution Tactics
The preferred method of delivery for people with varicose veins is natural childbirth, at first people use an elastic bandage or clothing pressed against the lower limb of the woman during labor. Patients with vulvovaginal varicose veins need special care during the long term with a protective episiotomy, as directed. When the foreign veins rupture, the damaged vessels are carefully sutured by repeatedly suturing the agglutination nodes. Caesarean section is recommended for patients at high risk of complications from severe thromboembolism and varicose veins of the vulva.
Forecast and Prevention
If promptly detected and treated adequately, the prognosis is positive. As a precaution, you should get enough sleep at night and rest periodically throughout the day in a supine position, with your feet placed on a solid surface at an angle of 30 °. Pregnant women with severe genetics should refuse to wear shoes with heels over 5 cm, limit the time to sit or stand and control weight gain.
To prevent varicose veins, walk daily, reduce salt intake and add vitamin preparations that help strengthen the vessel wall effectively. Patients with varicose veins are planning to become pregnant, according to the indication that surgical intervention is required to correct the disease.